14. SGD Solution
Here's my solution to the last quiz.
def sgd_update(trainables, learning_rate=1e-2):
"""
Updates the value of each trainable with SGD.
Arguments:
`trainables`: A list of `Input` nodes representing weights/biases.
`learning_rate`: The learning rate.
"""
# Performs SGD
#
# Loop over the trainables
for t in trainables:
# Change the trainable's value by subtracting the learning rate
# multiplied by the partial of the cost with respect to this
# trainable.
partial = t.gradients[t]
t.value -= learning_rate * partialTake a look at the last few lines:
# Performs SGD
#
# Loop over the trainables
for t in trainables:
# Change the trainable's value by subtracting the learning rate
# multiplied by the partial of the cost with respect to this
# trainable.
partial = t.gradients[t]
t.value -= learning_rate * partialThere are two keys steps. First, the partial of the cost (C) with respect to the trainable t is accessed.
partial = t.gradients[t]Second, the value of the trainable is updated according to Equation (12).
t.value -= learning_rate * partialThis is done for all trainables.
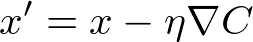
Equation (12)
With that, the loss decreases on the next pass through the network.
I'm putting the same quiz below again. If you haven't already, set the number of epochs to something like 1000 and watch as the loss decreases!
Question:
Start Quiz: